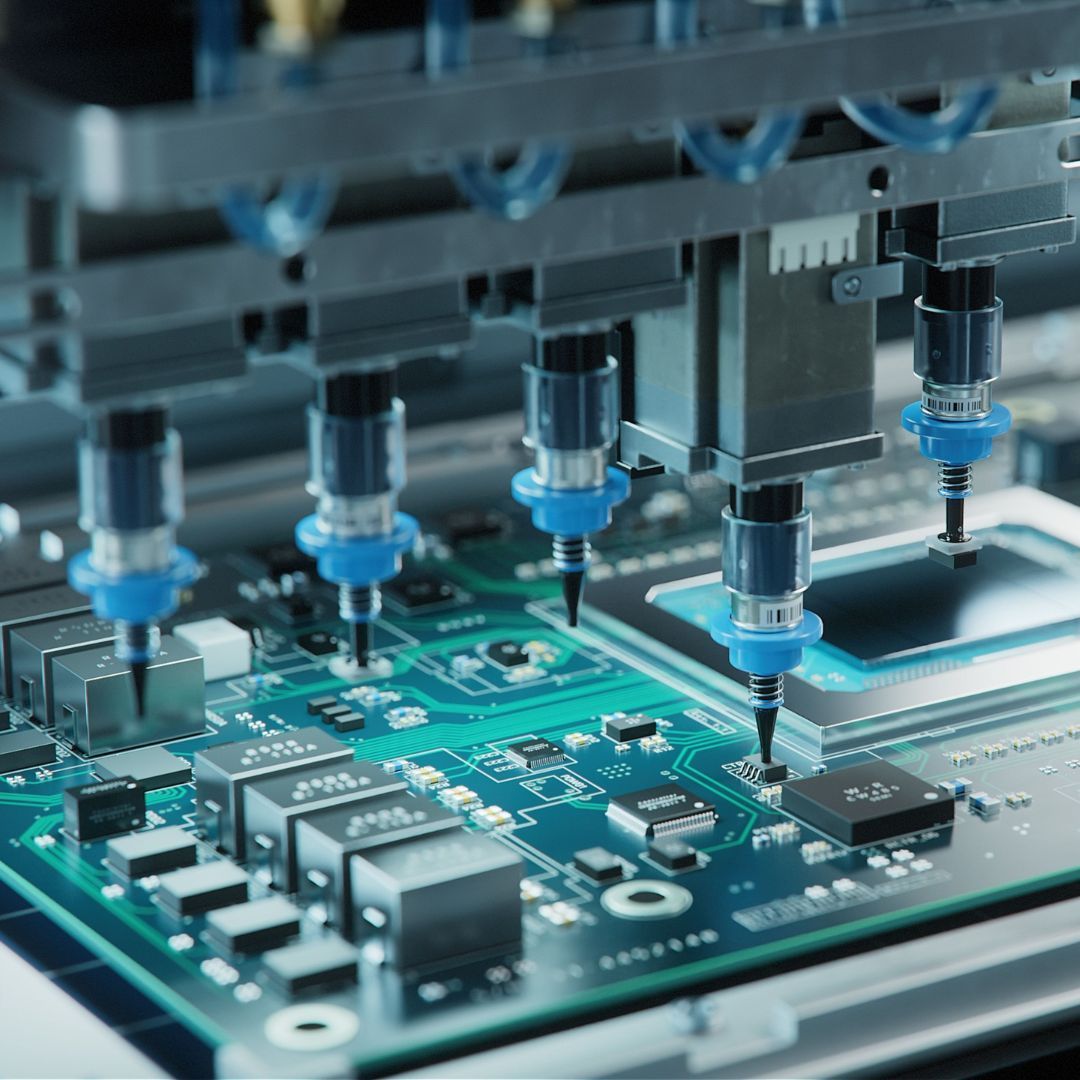
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assembly is a procedure that involves serious care and focus and is crucial to most electronic appliances.
In the modern age, it is arguable that assembling Printed Circuit Boards is one of the most important parts of how our society runs. Almost all electronics include a PCB, from personal computers to life-saving medical equipment, there is no denying how crucial they have become in our modern society. There are many practices in PCB assembly and this article will discuss these practices and how they can impact the reliability of our electronics.
Design For Assembly
Design For Assembly (DFA) is the practice of designing the Printed Circuit Board in the most optimal way possible. It considers the different aspects of PCB assembly in order to create the most efficient and effective PCB design. This can help manufacturers reduce assembly costs and streamline the production process.
When implementing DFA, one thing to consider is the placement of the components. By implementing DFA practices, the manufacturer can optimise the layout of the Printed Circuit Board and reduce the complexity of the design. This is beneficial as it makes the production process more streamlined, meaning higher productivity at a lower cost. The manufacturer can group related components together on the PCB, based on certain factors such as signal flow and thermal management. This makes the PCB assembly process more efficient.
DFA can also be effective when planning the testability and future maintenance of the PCB. Testability means planning ahead in the design for things like test points and probe access on the PCB. This allows for easier fault diagnosis during the assembly process which, in turn, speeds up the manufacturing process. When it comes to the maintenance of the Printed Circuit Board, DFA can help by adapting the design for easy removal of components if necessary. This may involve using connectors or sockets for certain components that may need frequent upgrades or maintenance.
SMT vs. THT
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Thru-Hole Technology (THT) are two of the key methods in PCB assembly. Both of these methods have their pros and cons, and the decision on which method to use relies on the individual circumstances of the Printed Circuit Board being made. In this section, we will compare these two methods and take a look at how they can help in creating reliable PCBs.
SMT involves placing the components directly onto the Printed Circuit Board. The components used are usually more compact which allows for a much more complex PCB design. This is beneficial for smaller electronics such as mobile phones. SMT is also compatible with pick-and-place machines, allowing for the PCB assembly process to be automated, making the process more efficient at a lower cost. Components used in SMT also have very high electrical performance, as well as easy accessibility to the components themselves.
THT uses larger, much more robust components. It involves threading leads through pre-drilled holes and soldering them to the other side. Contrasting to SMT, THT components are much more durable and mechanically secured. This allows the components to be more resistant to mechanical stress. THT assembly can be automated, but this process is much slower than the automation of SMT assembly. THT is more repairable and resistant to heat, which makes them much more durable and easy to deal with.
Soldering Techniques
Soldering is a key practice in the assembly of a Printed Circuit Board. It is the practice that creates electrical connections between the components and the PCB itself. There are many different techniques when it comes to soldering components onto a PCB and each has its own pros and cons. The techniques used are dependent on the different factors and performance needs of the PCB being assembled. Here is a list of different soldering techniques and how they can be beneficial:
Wave soldering - This is a bulk soldering technique used in THT components. The Printed Circuit Board is passed over a wave of molten solder to create solder joints. Wave soldering can be very cost-efficient however it can only be used in the THT method.
Reflow Soldering - This technique is used for surface mount components and is the most common technique of soldering. It involves using a solder paste to apply the components to the PCB. The assembly is then placed in a reflow oven where the heat can be controlled.
Hand soldering - This is a technique used for low-volume production. It involves using a soldering iron to individually place the components onto the PCB by hand. This type of soldering can provide great control and flexibility however it requires great skill and focus.
Vapour phase soldering - This technique is used by using boiling liquid to create a controlled vapour environment. The PCB is lowered into the vapour which solders the components. This technique provides even heating which is good for complex assemblies with varied components.
Selective soldering - This technique is used when specific components need to be soldered whereas other components need to stay unsoldered. A specialised machine is used to target certain components to be soldered via a mini wave or iron. This technique is useful for Printed Circuit Boards that have a mix of SMT and THT components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are many different practices when it comes to PCB assembly in order to build reliable electronics. DFA can be useful in the design stage of the Printed Circuit Board, allowing for the design to be specifically optimised for its desired purpose. There are also different types of methods in PCB assembly and soldering techniques. These different techniques can all be incredibly useful and are simply dependent on the requirements of the PCB.
M-Tek
At M-Tek Assembly we have decades of experience within the industry. We have achieved a
net-zero carbon footprint by using electric vehicles, and for every printed circuit board we build, we plant a tree. Contact one of our SMT and PCB assembly experts today for assistance. Call
01189 455377 or follow us on
Twitter to learn more about our products and services.
Recent Posts
Call Our Team
Want to find out more about our PCB assembly services? Speak to our team to find out how we can help you.
Join the Newsletter
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later