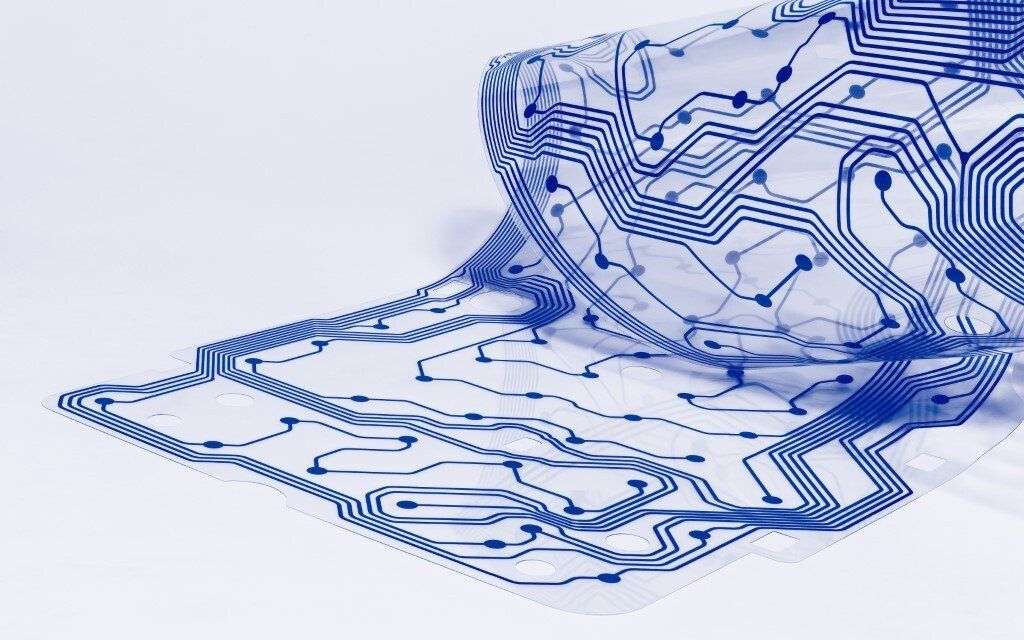
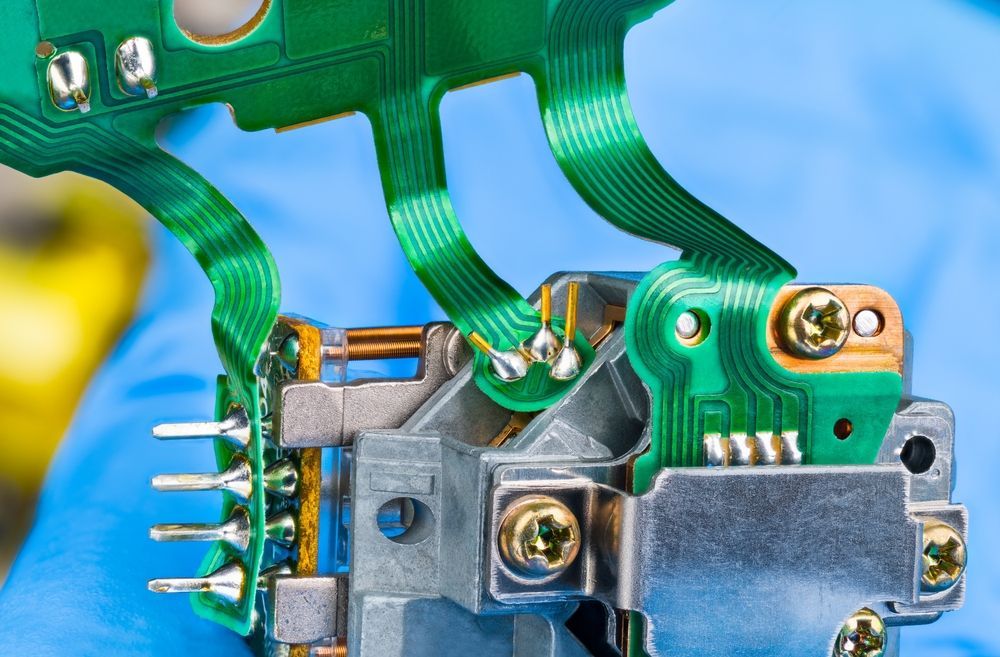
Flexible printed circuits, also known as flexible electronics, are a type of printed circuit board that has the ability to bend or flex. These circuits are made from thin, flexible materials such as polyimide or polyester, and they are used in a wide range of applications where traditional rigid circuit boards may not be suitable. Though people might not realize it, there is a lot more to know about these circuit boards.
Advantages of Flexible Printed Circuits
One of the main advantages of flexible printed circuits is their ability to be moulded into the desired shape, allowing them to fit into tight or irregularly shaped spaces. They are also lightweight, making them ideal for use in portable devices and wearable technology.
Additionally, the use of FPC can lessen the likelihood of human error during wiring, improving quality and lowering costs as a result. FPC technology helps to significantly reduce the application's size and weight, which is essential for the development of dependable, small, and highly integrated electronic devices.
Where are Flexible Printed Circuits used?
Flexible printed circuits are commonly used in a variety of industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, and military applications. They are also used in aerospace and space exploration, as their lightweight and flexible nature make them well-suited for use in these environments.
Types of Flexible Printed Circuits
There are several different types of flexible printed circuits, including single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer circuits. Single-sided circuits have conductive traces on one side of the circuit, while double-sided circuits have conductive traces on both sides. Multi-layer circuits have multiple layers of conductive traces, allowing for more complex circuits to be created.
How are they manufactured?
Flexible printed circuits are manufactured using a variety of techniques, including photolithography, etching, and lamination. Photolithography involves creating a pattern on a photoresist layer using light, while etching removes unwanted materials to create the desired circuit pattern. Lamination involves bonding multiple layers together using adhesive or heat and pressure.
There are several key considerations when designing and manufacturing flexible printed circuits. These include the thickness and material of the circuit, the size and pitch of the traces, and the type of conductor material used. The circuit must also be designed to withstand the mechanical stresses and environmental conditions it will be exposed to in its intended application.
Conclusion
Overall, flexible printed circuits are vital in a wide range of electronic devices and systems, offering a flexible and lightweight alternative to traditional rigid circuit boards. With their versatility and ability to be moulded into almost any shape, they will continue to play a significant role in developing new and innovative technologies.
M-TEK
M-tTEK is one of the leading UK CEM/EMS. We offer bespoke fast-track prototype services, medium/volume manufacture & complete product assembly, programming & test.
Fill in our online form here for more information regarding our services. Or, call us on 01189 455377 and speak to one of our experts today! Alternatively, follow us on
Twitter
to stay up to date with our services. For more information on flexible printed circuits,
read our previous blogs here.